3D Printer 3D model
In 2011, a biogel-powered printer printed a human kidney right during the TED conference.
A pair of years ago, Adidas announced a new model of sneakers that was printed on a 3D printer in 20 minutes. Recently, the company Ilona Mask SpaceX successfully tested the engines of the spacecraft, which also printed on a 3D printer.
In today’s world, 3D printing is not an amazing technology of the future, but a well-studied reality. It is used in architecture, construction, medicine, design, production of clothes and shoes and other fields.
At the request of a 3D printer, search engines give out hundreds of drawings and prototypes of varying complexity – from a soap box and a desk lamp to a car engine and even a residential building.
We will not bore you too much with dates and will just briefly retell the history of 3D printing.
In the early 80s, Dr. Hideo Kodama developed a rapid prototyping system using photopolymer – a liquid substance based on acrylic.
The printing technology was similar to modern: the printer printed the object according to the model, in layers.
The first 3D printer 3D model. The manufacture of physical objects using digital data was demonstrated by Charles Hull.
In 1984, when computers were still not very different from calculators, and before the release of Windows-95 was ten years old, he invented stereo lithography – the predecessor of 3D printing.
The technology worked like this: under the influence of an ultraviolet laser, the material solidified and turned into a plastic product.
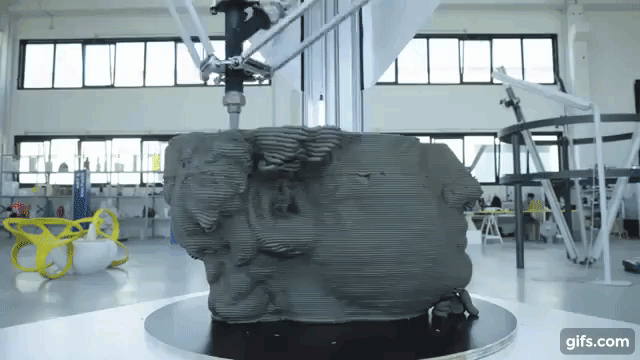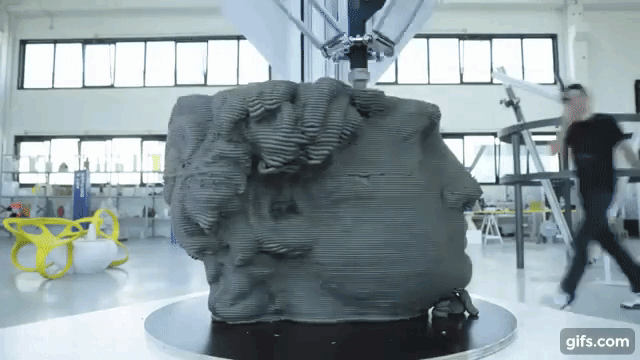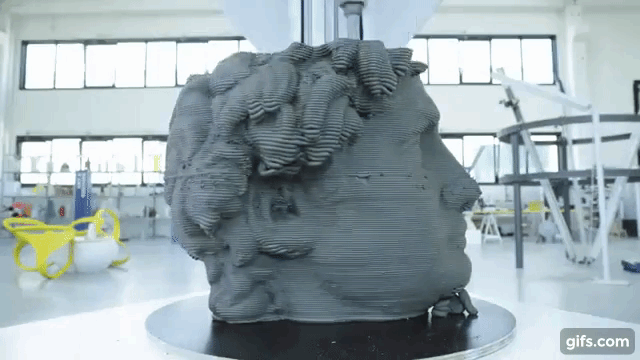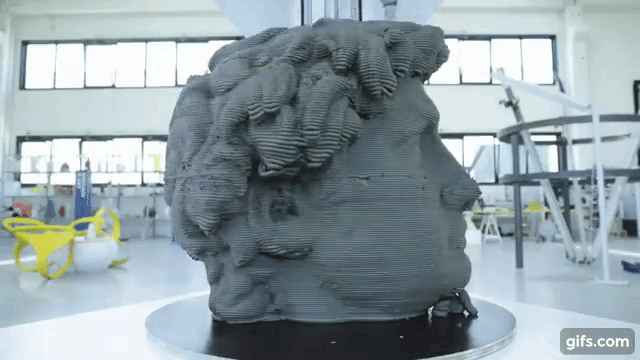
The form was printed on digital objects, and this became a boom among developers – now it was possible to create prototypes with lower costs.
Revolution in 3D printing. At the beginning of the 2000s, the market split into two directions: expensive complex systems and those that are available to everyone to print at home.
The technology began to be applied in specific areas: for the first time, a bladder was printed on a 3D printer, which was successfully implanted.
In 2005, the first 3D color printer with high print quality appeared, which created sets of parts for itself and its “colleagues”.
How does a 3D printer work?Basically, three-dimensional printers consist of the same parts and are similar in design to conventional printers.
The main difference is obvious: the 3D printer prints in three planes, and in addition to the width and height, depth appears.
Here are the parts that make up a 3D printer, not counting the case:
an extruder, or a print head – heats the surface, measures the exact amount of material using a gripping system and squeezes out semi-liquid plastic, which is fed in the form of threads;
a desktop (it is also called a work platform or surface for printing) – on it a printer forms parts and grows products;
linear and stepper motors –they drive the parts, are responsible for the accuracy and speed of printing;
clamps are sensors that determine print coordinates and limit moving parts. They need the printer not to go beyond the desktop, and make printing more accurate;
frame – connects all elements of the printer.

How to create 3D Printer 3D Model
The additive 3D-printing process is responsible for creating a three-dimensional product – this is when layers of material are superimposed on each other, from the bottom up, until a copy of the shape in the drawing is obtained. This is how plastic products are printed.
And photopolymer printing works using the technology of stereolithography (SLA): under the influence of a laser emitter, the photopolymers harden. In addition to plastic and photopolymer resins, modern 3D printers work with metal clay and metal powder.
Printing consists of continuous cycles that are repeated one after another – the next is applied to one layer of material, and the print head moves until a finished object is on the working surface. The printer itself removes printing waste from the desktop.
How 3D drawing works? The 3D printer prints the 3D model according to the 3D drawing: it is created on a computer in a special program, then saved in the STL format.
This file is output to the cutting program for the printer – it helps to set the model physical properties of the product, such as density. Next, the program converts the model into instructions for the extruder and uploads it to a printer, which begins to print the product.
How to program a 3D printer?
Short printer setup guide:
Select a 3D model. You can draw the product yourself in a special CAD editor or find a finished drawing – the Internet is full of models of varying complexity.
Prepare a 3D model for printing. This is done by the slice method (slice – part). For example, to print a toy, its model must be “split” into layers using the slicer programs and transferred to a printer. Simply put, the slicer shows the printer how to print an item: on what contour the print head moves, at what speed, what thickness of layers.
From the slicer, the 3D drawing is saved to a file called G-code. The computer downloads the file to the printer and starts 3D printing.
Can printed products be used?
Depending on the quality of the material, printer and final products 3D printer 3D models can be used or not. Often, home printers do not accurately convey the shape and color of an item.
Plastic products need additional processing: sometimes they are printed with burrs and defects and almost always with a ribbed surface.
There are several methods for surface treatment – not all are suitable for home use:
mechanical processing – grinding by hand, cutting burrs;
chemical – immersion in acetone, sandblasting, applying a special solution with a brush.
What can be printed on a 3D printer?
There are a number of promising areas in which 3D printing is already being used.
Rapid prototyping is one of the most popular areas in which 3D printing is used.
On 3D printers test models of prostheses, prototypes of medical corsets, bas-reliefs, Olympic equipment and many other items are made.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!